有一种说法,Netty只是网络通信框架,把Java Socket的API又封装了一次,使得你可以用最少的代码来完成网络通信这一任务。
一个高性能RPC框架最重要的四个点就是:传输协议,框架线程模型,IO模型,零拷贝。
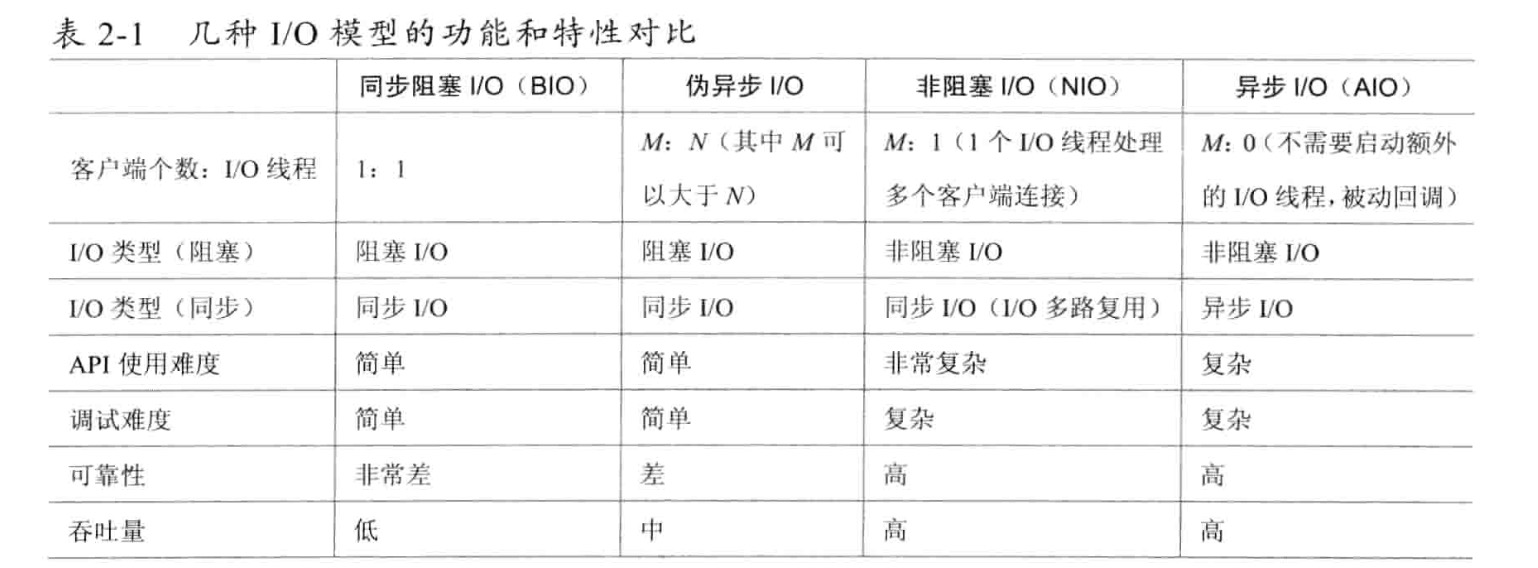
4种i/o之间的比较的
多路复用器 selector :selector 会不断地轮训注册在其上的channel,如果某个 Channel 上面有新的TCP连接接入、读写事件,这个Channel就处于就绪状态,会被Selector轮训出来,然后通过SelectorKey可以获取就绪Channel的集合,然后进行后续的 I/O 操作。
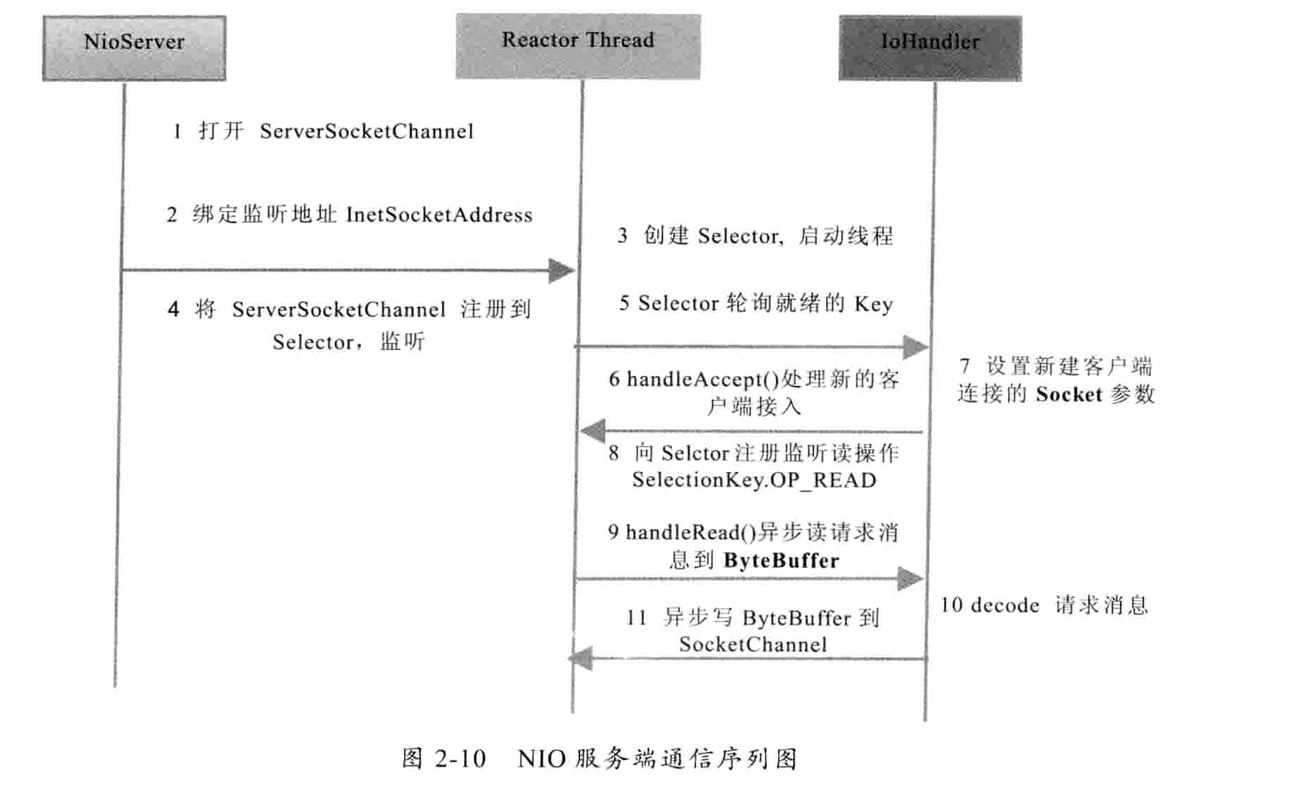
使用的nio实现时间服务器demo nio
/*
* Copyright 2013-2018 Lilinfeng.
*/
package com.phei.netty.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @date 2014年2月16日
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MultiplexerTimeServer implements Runnable {
//使用 netty 实现 i/o
private Selector selector;// 多路复用器
private ServerSocketChannel servChannel; //nio中的类
private volatile boolean stop;
/**
* 初始化多路复用器、绑定监听端口
*
* 一个多路复用器可以同时轮训多个 channel ,如果哪个
* channel上面有新的tcp连接接入,读和写事件,这个channel就处于
* 就绪状态,就会selector 轮训出来,然后通过selectionkey 可以获取就绪channel的
* 集合,进行后续的i/o操作。
*
* @param port
*/
public MultiplexerTimeServer(int port) { //构造方法
try {
selector = Selector.open();
servChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
servChannel.configureBlocking(false);
servChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
servChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //key 值是来标记状态的
System.out.println("The time server is start in port : " + port);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
public void stop() {
this.stop = true;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see java.lang.Runnable#run()
*/
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
handleInput(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (key != null) {
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null)
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 多路复用器关闭后,所有注册在上面的Channel和Pipe等资源都会被自动去注册并关闭,所以不需要重复释放资源
if (selector != null)
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
//接入状态 -- 读取状态 -- 处理数据
if (key.isValid()) {
// 处理新接入的请求消息
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// Accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
// Add the new connection to the selector
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
// Read the data
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
readBuffer.flip();//指针放到缓冲区的头部
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order : "
+ body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER"
.equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString()
: "BAD ORDER";
doWrite(sc, currentTime);
} else if (readBytes < 0) {
// 对端链路关闭
key.cancel();
sc.close();
} else
; // 读到0字节,忽略
}
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel channel, String response)
throws IOException {
if (response != null && response.trim().length() > 0) {
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
channel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
使用的netty实现时间服务器demo basic
/*
* Copyright 2013-2018 Lilinfeng.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.phei.netty.basic;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @date 2014年2月14日
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServer {
//使用netty来实现时间服务器
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// handler在初始化时就会执行,而childHandler会在客户端成功connect后才执行,这是两者的区别
// 等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel arg0) throws Exception {
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
new TimeServer().bind(port);
}
}
/*
* Copyright 2012 The Netty Project
*
* The Netty Project licenses this file to you under the Apache License,
* version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
* WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
* License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
package com.phei.netty.basic;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @author lilinfeng
* @date 2014年2月14日
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();//将消息发送队列中的消息写入到socketchannel 中发送给对方
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}
粘包/拆包
4种情况:
1.服务器端分两次读取到两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,没有粘包和拆包。
2.服务端一次接收到两个数据包,D1和D2粘合在一起,被称为TCP的粘包。
3.服务端分两次读取到两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1包和D2包的部分内容,第二次读取到D2的剩余内容,这部分被称为TCP拆包。
4.服务端分两次读取到两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1_1,第二次读取到D1剩余部分和D2的完整内容。
原因:
1.应用程序write写入的字节大小大于套接口发送缓冲区大小。
2.进行MSS大小的TCP分段。
3.以太网帧的payload大于MTU 进行IP分片。
tcp 粘包/拆包的问题 :LineBaseFrameDecoder + StringDecoder
//com.phei.netty.frame.correct.TimeServer中
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));//添加两个解码器
arg0.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());//然后不用考虑粘包,拆包的问题了
粘包:
消息定长,空位补空格;
在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,如FTP;
将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头里包含基本信息
解码器
分隔符和定长解码器:可以轻松的完成对消息的自动解码,而且不再需要考虑TCP粘包/拆包导致的读半包的问题。
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder :自动完成以分隔符做结束标志的消息解码
客户端,服务端都有:
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$_".getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,
delimiter));
FixedLengthFrameDecoder :自动完成对定长消息的解码
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(20));
编解码技术
java序列化是编解码技术的一种。
java序列化的主要目的:网络传输,对象持久化
java序列化是Java编解码技术的一种
无论是序列化后的码流大小,还是序列化的性能,JDK默认的序列化机制表现的都很差。
主流的编解码框架:google的protobuf
facebook的thrift
jboss Marshalling
使用netty提供的objectEncoder编码器和objectDecoder解码器实现对普通pojo对象的序列化
服务端:
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(
new ObjectDecoder(
1024 * 1024,
ClassResolvers
.weakCachingConcurrentResolver(this
.getClass()
.getClassLoader())));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqServerHandler());
}
});
@Sharable
public class SubReqServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
SubscribeReq req = (SubscribeReq) msg;
if ("Lilinfeng".equalsIgnoreCase(req.getUserName())) {
System.out.println("Service accept client subscrib req : ["
+ req.toString() + "]");
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp(req.getSubReqID()));
}
}
private SubscribeResp resp(int subReqID) {
SubscribeResp resp = new SubscribeResp();
resp.setSubReqID(subReqID);
resp.setRespCode(0);
resp.setDesc("Netty book order succeed, 3 days later, sent to the designated address");
return resp;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();// 发生异常,关闭链路
}
}
服务端在接收到数据之后,做出业务判断,然后向客户端发送回应,所以,客户端,服务端是相对的,客户端也可以是服务端,服务端也可以是客户端,都具备读写功能。
google的protobuf编解码 netty的protobuf编解码框架进行服务端,客户端开发
Jboss的Marshalling netty的Marshalling编解码框架进行服务端,客户端开发
netty多协议开发和应用
由于netty的http协议栈是基于netty的nio通信框架开发的,所以,netty的http协议也是异步非阻塞的
http是一个属于应用层的面向对象的协议
文件服务器:基于netty的http服务端应用开发
http+xml 协议栈 :
a.http服务端对http+xml请求消息进行解码,解码成请求pojo
b.客户端对http+xml响应消息进行解码,解码成响应pojo
http+xml 协议栈的开发demo,展示了如何基于netty提供的http协议栈做二次定制开发
jibx 是为java设计的xml数据绑定框架
webSocket
webSocket连接本质上是一个tcp连接,
客户端首先要向服务端发起一个http请求,其中附加了头信息。服务器端解析这些附加的头的信息,然后生成应答信息返回给客户端。这样连接就建立起来了。双方可以通过这个通道自由的传递信息,这个通道会持续存在直到客户端或者服务端的某一方主动关闭连接。
webSocket将网络套接字引入到了客户端和服务端,浏览器和服务器之间可以通过套接字建立
持久的连接,双方随时都可以护发数据给对方,而不是之前由客户端控制的一请求一应答的模式。
http协议的弊端:
1.http协议为半双工协议。意味着数据可以在客户端和服务端两个方向上传输,但是不能同时传输。
它意味着在同一时刻,只有一个方向上的数据传输。
2.http消息冗长而繁琐。
3.针对服务器推送的黑客攻击。例如长时间轮询。
为了建立一个WebSocket连接,客户端浏览器首先要向服务器发起一个http请求,这个请求和通常的http请求不同,包含一些附加的头信息。服务端解析这些附加的头信息之后,生成相应返回给客户端,客户端和服务端的webSocket连接建立起来了,双方就可以通过这个连接通道自由的传递信息,并且这个连接会持续存在直到客户端或者服务端的某一方主动关闭连接。
使用netty开发websocket服务端。
UDP协议开发
udp是面向无连接的,不可靠的数据报投递服务。
与TCP相比,UDP不存在客户端和服务端的实际连接
netty实现文件传输
绝大部分的私有协议传输层都是基于tcp/ip,所以利用netty的nio tcp协议栈可以非常
方便的进行私有协议的定制和开发。